Description
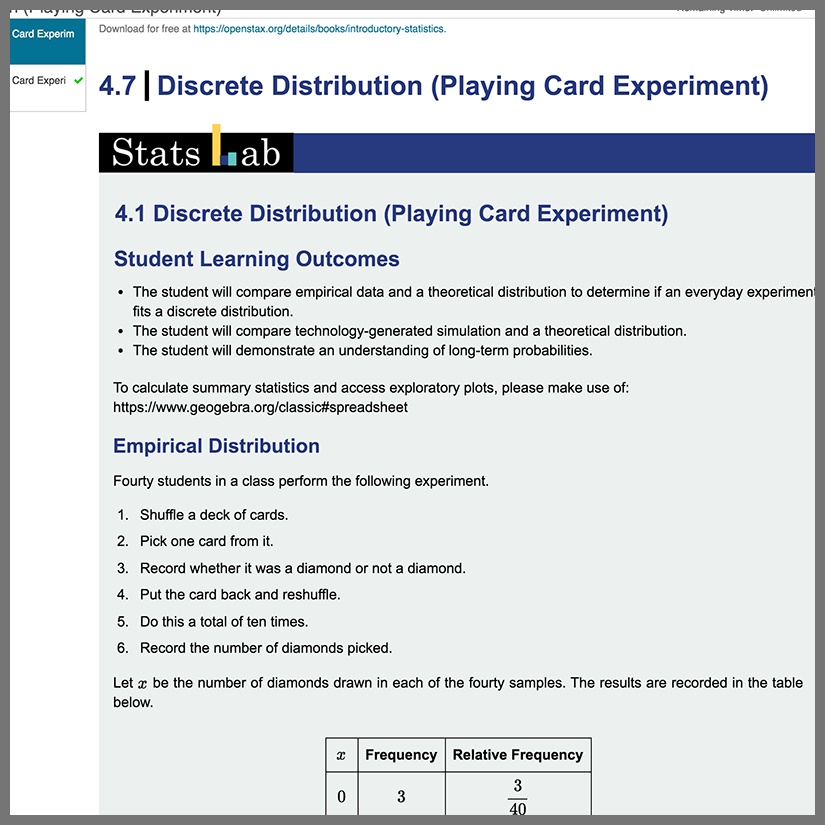
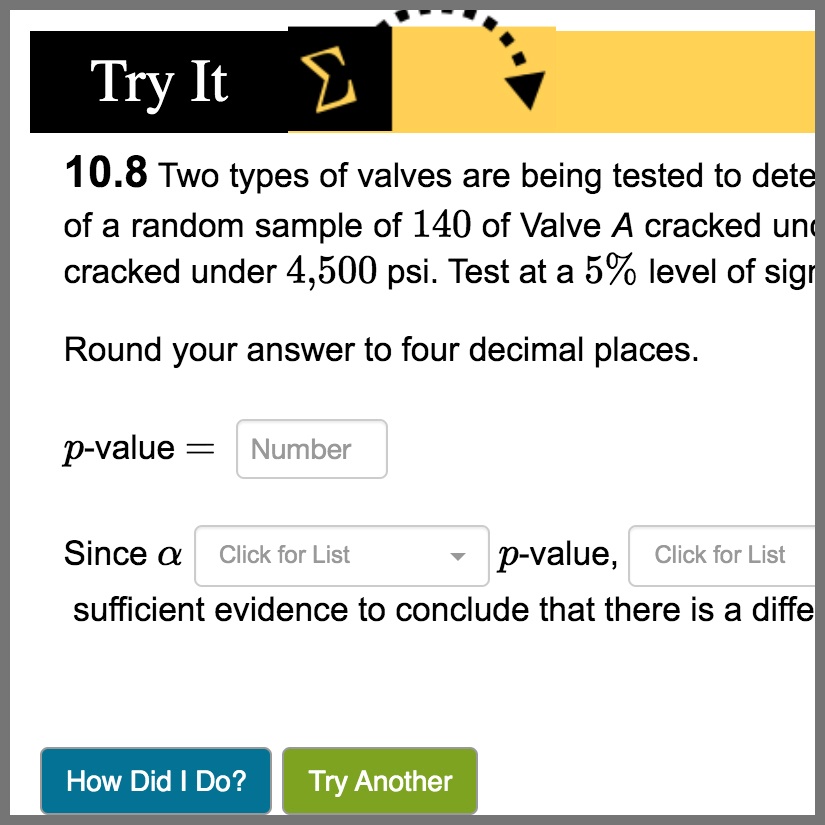
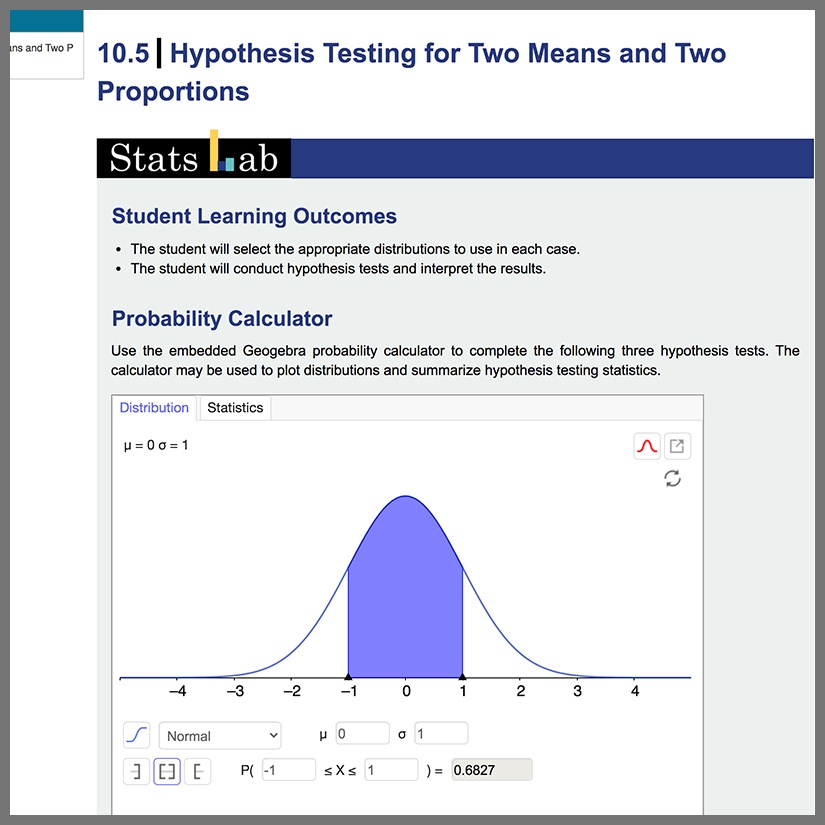
The Introductory Statistics Content Pack is an entire OpenStax textbook that you can use as a customizable starting point to a complete statistics course in Möbius. While following scope and sequence requirements of a one-semester introductory statistics course, this material assumes some knowledge of intermediate algebra and is geared towards students majoring in fields other than mathematics or engineering. This Content Pack focuses on statistics application over theory and includes: innovative practical applications that make the text relevant and accessible, collaborative exercises, technology integration problems, and statistics labs with randomization algorithms. This customizable resource includes all traditional OpenStax features such as chapter introductions, sections, review material, and practice tests, and has been enhanced with Möbius capabilities including algorithmic questions, in-lesson questions with unlimited practice, helpful hints, and immediate feedback.
How does Möbius take OpenStax to the next level?
All chapter sections delivered as Möbius lessons with checkpoint questions embedded right inside of lessons.
Learn how Möbius’ unique STEM question types provide the best STEM learning experience.
Deliver OpenStax exercises using over 50 configurable assessment properties.